Details
Overview
- Laminar flame speed is a key parameter in engine design/performance, contains the information of reactivity/diffusivity/exothermicity, and serves as a good validation of kinetic mechanisms.
- Surrogate fuels are the alternative to gasoline in many combustion applications; there is lack of combustion characteristics, data, and performance in surrogates fuels
Aim
- The flat flame method has the advantages of producing a well-defined, 1-D flat flame free of stretch, and requiring less complicated experimental setup
- To determine the laminar flame speed, a technique (as shown in Fig. 1) with heat extraction through the cooling water, similar to that described in Botha and Spalding (1954), is employed and the adiabatic laminar flame speed is
obtained by extrapolation.
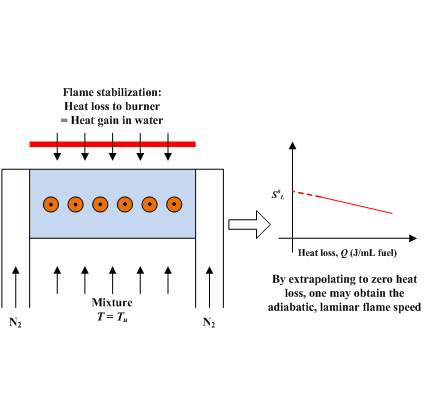 Figure 1. A Schematic of heat extraction
Figure 1. A Schematic of heat extraction
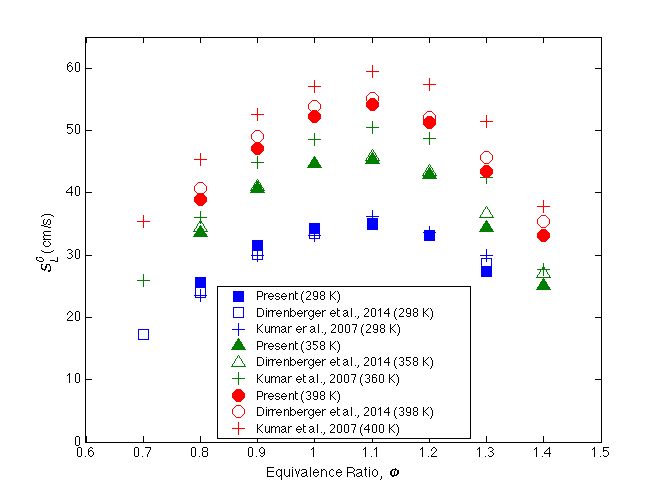
Figure 2. The laminar flame speeds of iso-octane


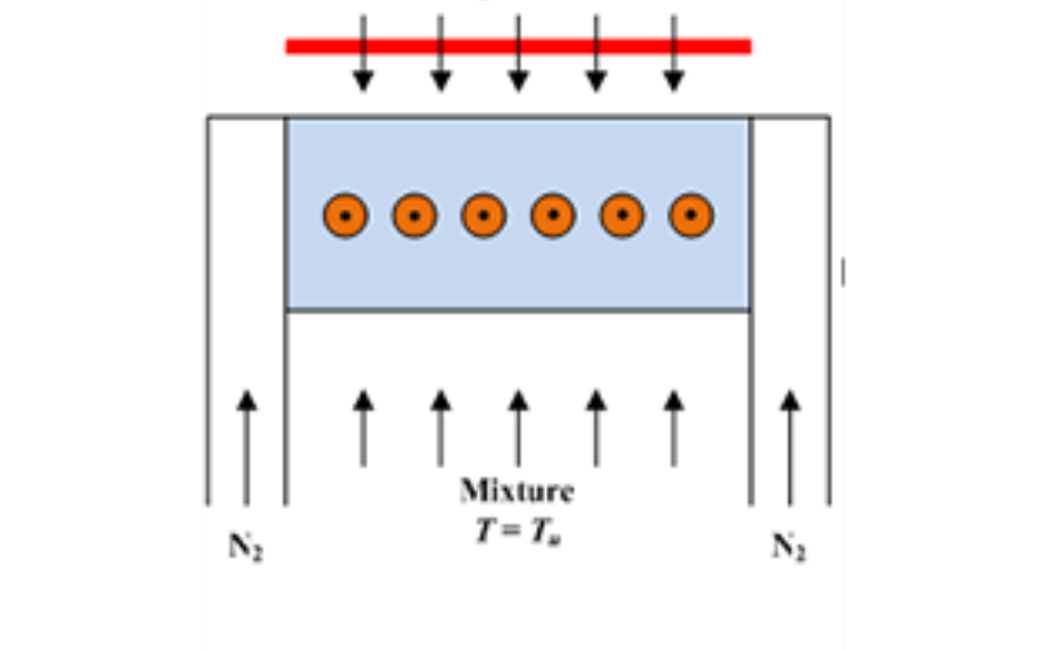
 Figure 1. A Schematic of heat extraction
Figure 1. A Schematic of heat extraction
